What is FOB Destination? Meaning, Terms, Who Pays?
These laws use specific terms outlined in detailed contracts to define delivery time, payment terms, and when the risk of loss shifts from the seller to the buyer. Known as Incoterms, these terms are published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) to help navigate the complexities of international trade and differing country laws. The term “shipping point” might seem straightforward, but when paired with FOB, it takes on a much more nuanced meaning. A shipping point generally refers to the location where goods begin their journey to the final destination. This could be a seller’s loading dock, a shipping port, or an originating port where a freight forwarder consolidates shipments.

Understanding FOB Shipping
The seller also obtains the necessary documentation, licenses, and inspections that may be required. The specific definitions vary somewhat in every country, but both contracts generally specify origin and destination information that is used to determine where liability officially begins and ends. They also outline the responsibilities of buyers to sellers, as well as sellers to buyers.
Benefits of FOB Origin
Instead, use FCA (Free Carrier), CPT (Carriage Paid To), and CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To), which are the correct alternatives as they are meant for containerised freight. CIF stands for Cost, Insurance and Freight, whereas FOB stands for Free on Board. Both CIF and FOB are agreements used for international shipping when products are transported between a seller and buyer. The main difference between CIF and FOB is who is responsible for the products in transit. FOB also determines when a business will record a sale for accounting purposes. If a shipment is designated as FOB Shipping Point, the sale will be recorded in the accounting system as soon as the shipment leaves the seller’s dock.
Consider shipping costs
- This includes any expenses incurred at the destination port, such as customs fees.
- The accounting entries are often performed earlier for a FOB shipping point transaction than a FOB destination transaction.
- When the terms state “Freight collect, FOB origin” the buyer is responsibly accountable for both the products and the freight charges.
- FCA or “free carrier” means a seller is obligated to deliver goods to a specified location or carrier where the buyer will take responsibility for transit.
- Use Skynova’s proven software solutions for small business and free templates to simplify and expedite the process of earning customers’ business and getting paid.
Anyone who ships goods or provides services can benefit from using Skynova’s invoice template. The free, easy-to-use template enables you to quickly create sales invoices, giving you more time to spend on crucial aspects of running and growing your business. Jeff could sue Ann for new parts because the title of the goods during transit would still belong to Ann. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. FOB is important because it has shipping, liability, and accounting implications.
- That’s because the seller may use a transport carrier of their choice who may charge the buyer more to increase the profit on the transaction.
- The term FOB Shipping Point indicates that the responsibility and ownership of the goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer at the seller’s location (or point of origin).
- Also, under FOB destination conditions, the seller is liable for the merchandise’s transportation costs.
- FOB, while advantageous in many ways, comes with inherent transit risks, especially for the party responsible during the shipping.
- CIF is an expense paid by the seller to cover the freight costs, insurance, and shipping of a buyer’s order while being transported to the buyer’s destination.
What Is the Difference Between CIF and FOB?
Whether the buyer or seller pays for shipping, they will also have to enter those transportation costs in their account ledger. These freight costs can include the labor needed to handle and load the goods at the shipping dock, the cost of transporting fob shipping point them to the vessel, shipping, and insurance. In modern domestic shipping, the term is used to describe the time when the seller is no longer responsible for the shipped goods and when the buyer is responsible for paying the transport costs.
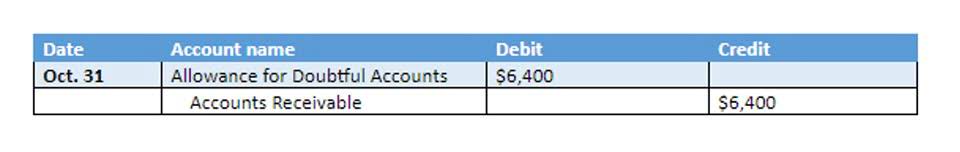
The term FOB shipping point is a contraction of the term Free on Board Shipping Point. It means that the customer takes delivery of goods being shipped to it by a supplier once the goods leave the supplier’s shipping dock. Since the customer takes ownership at the point of departure from the supplier’s shipping dock, the supplier should record a sale at that point. In addition, the customer should insure the goods during the in-transit period. The choice between FOB Origin and FOB destination depends on the specific needs of both parties.
In essence, this means the sale is finalized the moment the shipping carrier takes the goods away. So, the buyer pays for the goods before they are received and usually bears the cost of shipping and liabilities of transportations, including loss, damage, or theft. Conversely, with FOB destination, the title of ownership transfers to the buyer once the goods reach the buyer’s loading dock, post office box, or office building. This means the seller retains ownership and responsibility for the goods during the shipping process until they’re delivered to the buyer’s specified location.


Essentially, when the seller delivers the goods and ships them, they’re taking care of all the transportation costs up to the final destination. This often involves specifying in the shipping documents that freight is prepaid. In FOB shipping points, if the terms include “FOB origin, freight collect,” the buyer pays for freight costs. If the terms include “FOB origin, freight prepaid,” the buyer is responsible for the goods at the point of origin, but the seller pays the transportation costs. The critical juncture in any FOB agreement is often the shipping point—whether it’s a loading dock, shipping port, or any originating port.
FOB destination definition

This includes ensuring the goods arrive at the FOB destination in a satisfactory condition. The FOB term refers to the moment where a business that is shipping products is no longer responsible for the items. In this variation, the price is set at the shipping point, encompassing all costs up to that point but not beyond. FOB pricing gives clarity about how much the buyer will pay before additional shipping costs. The free, easy-to-use template allows you to rapidly make sales invoices, freeing up time to focus on other important parts of your business.
